- About Us
-
-
-
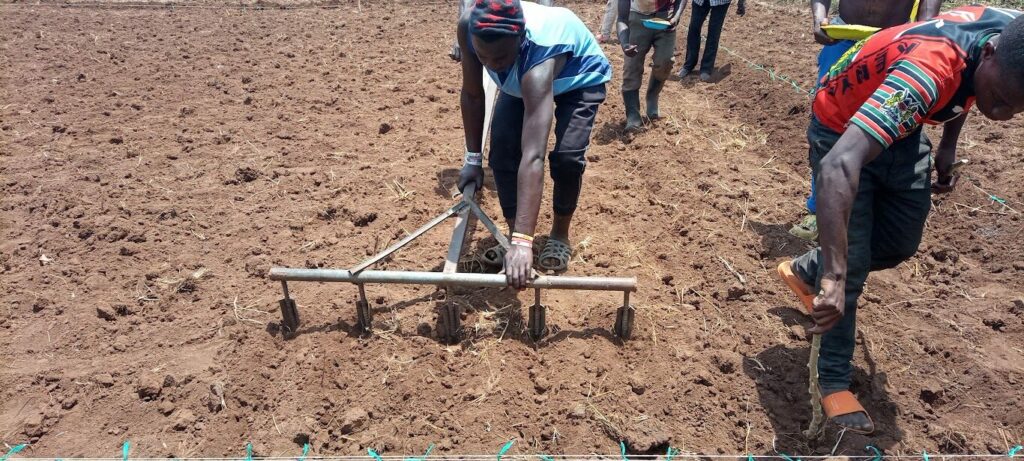
The Heart Of Agriculture
Seed Co has 85 years of experience in the production and supply of certified high-yielding seed varieties bred in Africa for African climatic and geographic conditions.
-
-
- Products
-
-
-
The Heart Of Agriculture
Our Seed Co maize varieties are specially bred for various ecological regions across Africa, assuring farmers of quality certified seeds and high yields.
-
-
-
-
- Farmers Hub
-
-
-
The Heart Of Agriculture
In addition to an extensive range of maize hybrid seed, Seed Co also markets seed for wheat, soya beans and vegetable seeds.
-
-
- Innovations
-
-
-
The Heart Of Agriculture
Seed Co has maintained a strong market share among communal and commercial farmers from years of intensive investment in Research and Development.
-
-
- Media
-
-
-
The Heart Of Agriculture
Our Seed Co maize brands are specially bred for various ecological regions across Africa, assuring farmers of the best in class quality seeds and high yields which result in bumper harvests every season.
-
-
- Contact Us
 Malawi
Malawi Seed Co Group
Seed Co Group Angola
Angola Botswana
Botswana DRC
DRC Kenya
Kenya Nigeria
Nigeria South Africa
South Africa West & Central Africa
West & Central Africa Tanzania
Tanzania Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe





